Guide to NFS on Linux
Step-by-step guide to NFS in Linux, from basic to advanced concepts, with practical examples and command explanations for each stage.
Guide to NFS on Linux
What is NFS?
NFS (Network File System) allows Linux systems to share directories and files with others over a network. It is commonly used for centralizing storage and making files accessible to multiple machines.
NFS Architecture
- NFS Server: The machine that shares its directories.
- NFS Client: The machine that mounts and accesses the shared directories.
Prerequisites
- Two Linux machines on the same network.
Setting Up NFS: Step-by-Step
1. Install NFS Packages
On Ubuntu/Debian:
1
2
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server nfs-common
On CentOS/Fedora/RHEL:
1
sudo yum install nfs-utils
nfs-kernel-server: Provides the NFS server functionality.nfs-common/nfs-utils: Provides client utilities.
2. Create a Directory to Share
1
2
3
sudo mkdir -p /srv/nfs/shared
sudo chown nobody:nogroup /srv/nfs/shared
sudo chmod 777 /srv/nfs/shared
chownandchmod: Set permissions so all clients can access it.
3. Configure NFS Exports
Edit the exports file:
1
sudo nano /etc/exports
Add a line like:
1
/srv/nfs/shared 192.168.1.0/24(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)
rw: Read/write access.sync: Writes changes to disk before replying.no_subtree_check: Disables subtree checking for better performance.Replace 192.168.1.0/24with your networksubnet.
4. Export the Shared Directory
1
sudo exportfs -ra
-ra: Re-exports all directories listed in/etc/exports.
5. Start and Enable NFS Server
1
sudo systemctl enable --now nfs-server
- Starts the NFS server and enables it at boot.
6. Adjust Firewall (if enabled)
On Ubuntu:
1
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.0/24 to any port nfs
192.168.1.0replace with your own ip/subnet ip
On CentOS/Fedora:
1
2
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=nfs
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
- Allows NFS traffic through the firewall.
7. Check NFS Exports
1
showmount -e
- Lists exported directories on the server.
NFS Client Configuration
1. Install NFS Client Utilities
On Ubuntu/Debian:
1
sudo apt install nfs-common
On CentOS/Fedora/RHEL:
1
sudo yum install nfs-utils
- Installs the client-side tools.
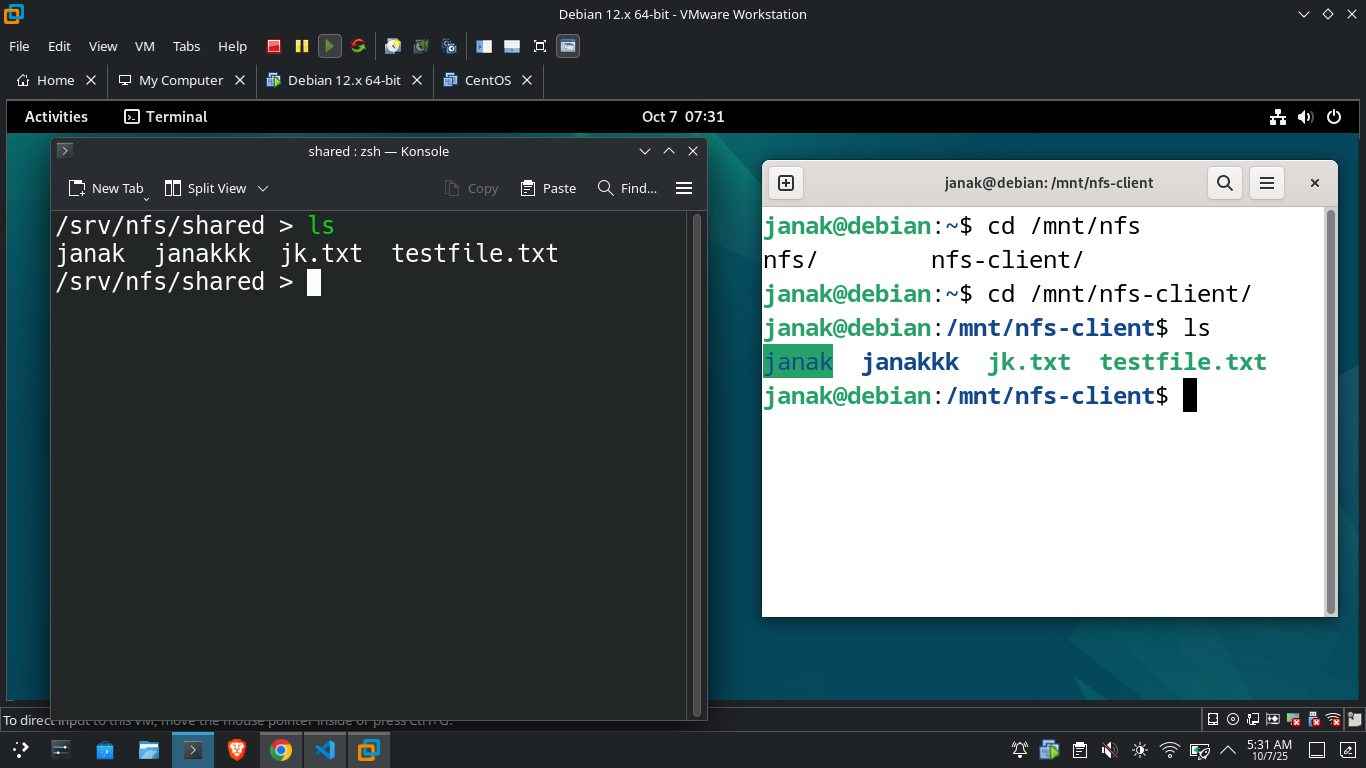
2. Mount the NFS Share
1
2
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/nfs-client
sudo mount -t nfs 192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/shared /mnt/nfs-client
- Replace
192.168.1.100with the server’s IP address. /mnt/nfs-clientis the local mount point.
3. Make the Mount Permanent
Edit /etc/fstab:
1
sudo nano /etc/fstab
Add:
1
192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/shared /mnt/nfs-client nfs defaults 0 0
- Ensures the share mounts at boot.
4. Unmount the NFS Share
1
sudo umount /mnt/nfs-client
- Unmounts the share from the client.[10]
Export Options
ro: Read-only access.no_root_squash: Allows root on client to act as root on server (use with caution).all_squash: Maps all client users to anonymous user.anonuid/anongid: Set UID/GID for anonymous users.
NFS Versions
- NFSv3: Widely supported, stateless.
- NFSv4: Improved security, stateful, supports ACLs and pseudo-root.
Security Best Practices
- Restrict access to trusted IPs.
- Use firewalls to limit NFS ports.
- Prefer NFSv4 for better security features.
Troubleshooting
- Check NFS status:
sudo systemctl status nfs-server - View logs:
journalctl -xe | grep nfs - Test connectivity:
showmount -e 192.168.1.100 - Remount all:
sudo mount -a - Check permissions: Ensure directory and export permissions are correct.
Example: Full Workflow
On Server:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server
sudo mkdir -p /srv/nfs/shared
sudo chown nobody:nogroup /srv/nfs/shared
sudo chmod 777 /srv/nfs/shared
echo "/srv/nfs/shared 192.168.1.0/24(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)" | sudo tee -a /etc/exports
sudo exportfs -ra
sudo systemctl enable --now nfs-server
On Client:
1
2
3
sudo apt install nfs-common
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/nfs-client
sudo mount -t nfs 192.168.1.100:/srv/nfs/shared /mnt/nfs-client
- Now, files placed in
/srv/nfs/sharedon the server will appear in/mnt/nfs-clienton the client.
Thank You
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.